
Coconut oil, once limited to specialist Asian food stores, is now widely available in health food stores, online and supermarkets. Its popularity is due to an increasing number of media reports concerning its health benefits.
While some of the health claims are based on anecdotal evidence, many are grounded in science. Indeed, coconut oil has several properties that set it apart from other vegetable oils.
Before we begin to examine these, it’s important to address the reasons that coconut oil was formally considered unhealthy.
Saturated Fat – The Heart Disease Myth
Coconut oil is made up of several different types of fatty acids:
- Lauric 48%
- Myristic 16%
- Palmitic 9.5%
- Decanoic 8%
- Caprylic 7%
- Oleic 6.5%
- Other 5%
All of these are saturated fats with the exception of oleic acid, making coconut oil around a 90% saturated fat. (For comparison, butter is 57% saturated fat and lard is 32% saturated fat.) For the last four decades, health authorities have advised the public to avoid saturated fats due to an unproven theory linking it to high cholesterol, heart disease and weight gain.
Ironically, as a result of the campaign demonizing saturated fats, the processed food industry and many individuals switched from natural saturated fats like butter to industrially produced trans fats – now known to raise levels of LDL ‘bad cholesterol’ and increase the risk of heart disease.
Current research is earnestly questioning the link between saturated fat and heart disease. An assessment published in the journal Nutrition uncovered several flaws in the Dietary Guidelines for Americans Advisory Committee’s 2010 Report. The authors point out that the committee’s conclusions about saturated fat are based on an incomplete body of relevant science and science which is inaccurately represented or summarized.
Several very large meta-analyses have failed to find a link between saturated fat and cardiovascular disease. A 2015 systematic review published in the BMJ analyzed data from 50 studies examining links between dietary saturated fat and/or trans fats and various health outcomes.
Researchers concluded that saturated fats are not associated with all causes of mortality, cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease, ischemic stroke or type 2 diabetes. In contrast, trans fats are associated with all causes of mortality, coronary heart disease and deaths from coronary heart disease.
A Different Type of Saturated Fat
The predominant form of fat in the standard Western diet is long-chain triglycerides (LCTs). These are absorbed into the blood stream and transported into cells to be metabolized or stored as body fat.
Coconut oil is primarily made up of medium-chain triglycerides or MCTs (also known as medium-chain fatty acids). Because MCTs have fewer carbon bonds than LCTs, they are processed differently. MCTs are transported directly to the liver where they are rapidly metabolized for energy.
Coconut oil contains two of the three MCTs found in food: lauric acid and caprylic acid. It is the best dietary source of MCTs, with about eight grams per tablespoon.
Research has shown that replacing dietary LCT with MCT causes a rise in energy expenditure and a lower body fat mass index. Evidence suggests that MCTs also help to reduce inflammation and protects the liver from toxins.
7 Science-Backed Benefits of Coconut Oil
1. Cuts Abdominal Fat

Abdominal obesity, characterized by an apple-shaped figure or a beer belly, is a better predictor of an increased risk for disease than overall BMI.
The National Institutes of Health‘s obesity guidelines state that women with a waist circumference greater than 35 inches and men with a waist circumference greater than 40 inches are at high risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. The medium chain triglycerides in coconut oil seems to particularly target abdominal fat.
In a randomized clinical trial, 40 abdominally obese women were put on a 12-week diet and exercise regime. One group received daily supplements containing soy bean oil and the other received coconut oil supplements. Both groups lost weight, but only the coconut oil group showed a significant reduction in waist circumference. The coconut oil group also had increased levels of HDL ‘good cholesterol’. In the soy bean oil group, LDL ‘bad cholesterol’ increased and HDL diminished.
A 6-month clinical trial examined the effects of coconut oil on 116 male and female patients with coronary artery disease. All of the participants were put on a cholesterol lowering diet. After a 3-month run-in period, one group of patients were given 13 ml of extra virgin coconut oil daily and the other continued with the diet as usual. The diet reduced body weight for both groups, however, the addition of coconut oil led to a significant reduction in waist circumference and a significant increase in HDL.
Recommended:
2. Raises Your HDL ‘Good Cholesterol’ Levels

High density lipoprotein (HDL) is a protein that wraps around cholesterol in the cells and transports it to the liver for recycling. It helps maintain the inner walls of arteries by removing fat deposits that can lead to atherosclerosis.
High levels of HDL are associated with a decreased risk of heart disease and stroke. Coconut oil contains myristic acid which has been shown to raise levels of HDL, along with other fatty acids which have no effect on cholesterol.
In a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 12 healthy men were served two diets which were identical except for the type of fat included. One diet contained 40% of calories from palmitic acid (the main component of palm oil) and one contained 40% of calories from myristic acid. After 3 weeks on one diet, the men took a 5-week break and then spent 3 weeks on the other diet. Blood tests showed that both diets had a similar effect on LDL and total cholesterol. However, the myristic acid diet raised HDL by 8% and lowered the ratio of LDL to HDL.
Another study conducted in the Philippines, where coconut oil is commonly used in cooking, examined its effects on cholesterol. A cohort of 1,839 women aged 35–69 filled in two 24-hour dietary questionnaires on consecutive days. Researches categorized their intake of coconut oil as low, medium or high. Blood tests showed that coconut oil did not elevate total cholesterol or triglyceride levels.
In pre-menopausal women, moderate or high coconut oil intake was associated with significantly higher HDL compared to women with low coconut oil intake.
Recommended:
3. Promotes Healthy Skin

Coconut oil has several properties that can help improve your complexion. It is an emollient which increases skin hydration, making it an effective moisturizer for dry skin. It also acts as a natural sunscreen. The antibiotic properties of coconut oil can help to treat acne, speed skin healing and prevent infection.
Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun breaks down collagen and elastin in the skin. Over-exposure to UV light is a major cause of wrinkles and premature skin aging. Spectrophotometer testing indicates that coconut oil blocks out about 20% of UV rays.
One study evaluated the UV absorption ability of 16 herbal oils in terms of sun protection factor (SPF) values. Olive oil came out on top with an SPF value of 7.5, but coconut oil was a close second with an SPF value of 7.1.
A study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology investigated the therapeutic potential of lauric acid for treating acne. Acne outbreaks are commonly triggered by an overgrowth of Propionibacterium acnes bacteria. Antibiotics such as benzoyl peroxide are widely prescribed for acne patients. Laboratory tests showed that lauric acid prevented the growth of P. acnes at concentrations 15 times lower than benzoyl peroxide and was not toxic to human sebaceous glands. In a follow-up study, researchers injected mouse ears with P. acnes. Application of lauric acid effectively decreased the number of acne-causing bacteria and reduced inflammation in the ear.
Another rodent study evaluated the effects of coconut oil on wound healing. Researchers found that rats whose wounds were treated with virgin coconut oil healed much faster than a control group whose wounds were untreated. Analysis of skin wounds showed that the coconut oil reduced markers of inflammation, increased antioxidant enzyme activities and encouraged collagen production.
Method: To moisturize your skin and protect it from the sun, wash your face, pat dry and apply coconut oil with your fingers. Wait for a minute or two to allow your skin to absorb the oil, then use a cotton ball to remove any shiny excess.
To treat acne, insect bites, and minor wounds or burns, dab a little coconut oil directly over the inflamed skin.
Recommended:
4. Treats Dermatitis
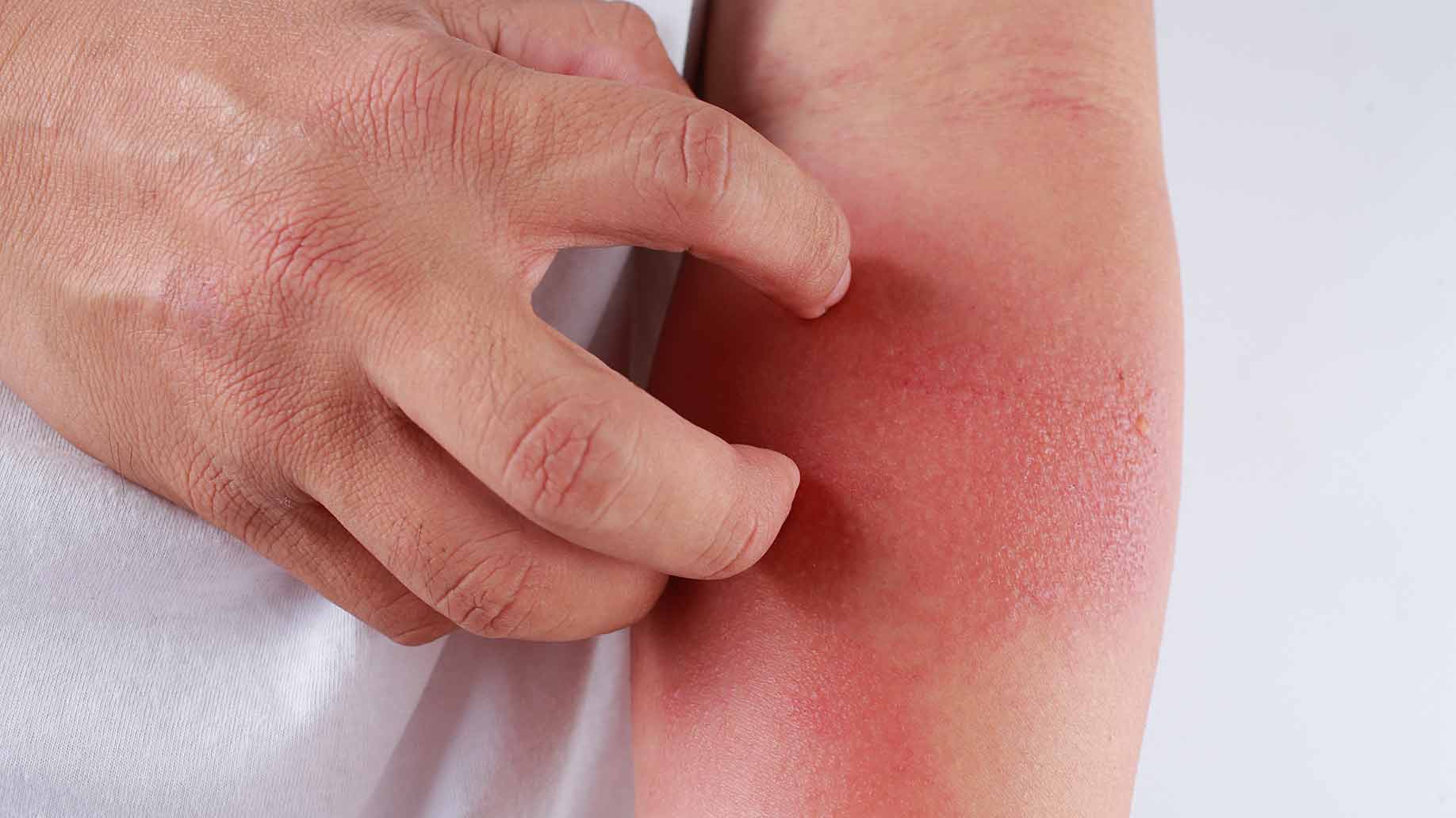
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin that causes it to become dry, red, swollen and cracked. It affects approximately 10% of children under ten and 2% of adults.
People with atopic dermatitis are especially vulnerable to skin infections caused by the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Coconut oil coats and penetrates the skin to moisturize it. The MCTs and antioxidants in the oil helps to reduce inflammation, while the lauric acid has antibacterial properties.
A randomized controlled trial examined the effects of topical virgin coconut oil on 117 pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. The children, aged 1–13, were divided into two groups. Half received bottles of virgin coconut oil and half received bottles of mineral oil. Parents were instructed to apply the oil to their child’s skin twice a day for 8-weeks. In the coconut oil group, 47% of patients achieved moderate improvement in dermatitis symptoms and 46% showed an excellent response. In the mineral oil group, 34% showed moderate improvement and only 19% achieved an excellent response. Coconut oil was also significantly better than mineral oil at improving skin hydration and preventing water loss through the skin.
A trial published in the journal Dermatitis compared the effects of virgin coconut oil and virgin olive oil on dermatitis symptoms and Staphylococcus aureus infections. Adult atopic dermatitis patients were randomized to apply either virgin coconut oil or virgin olive oil twice daily to two non-infected sites on their skin. After 4-weeks, 5% of the coconut oil group tested positive for Staphylococcus aureus compared to 50% for the olive oil group. The coconut oil group also showed a greater improvement in dermatitis symptoms.
Recommended:
5. Improves Oral Health

When coconut oil is used as a mouthwash, the lauric acid reacts with the alkalis in the saliva to form a soap-like substance which coats the teeth and reduces plaque adhesion.
Lauric acid also has antimicrobial properties. It can help to control oral bacteria including Streptococcus mutans, the most common cause of tooth decay.
In a study published in the Archives of Oral Biology, researchers compared the antibacterial effects of coconut oil to chlorhexidine, the active ingredient in antiseptic mouthwash. A total of 50 girls aged 8-12 were randomly assigned to use coconut oil or a chlorhexidine rinse after brushing their teeth in the morning. Under adult supervision, they were given 5-10 ml of the assigned solution and asked to swish it all throughout their mouths and to move it between their teeth. After 30 days, their plaque and saliva were tested for Streptococcus mutans. Coconut oil was just as effective as chlorhexidine mouthwash in reducing oral bacteria.
A pilot study assessed the effects of coconut oil on plaque and gum disease. Researchers recruited 60 participants aged 16-18 with plaque-related gingivitis. The subjects were instructed to perform oil pulling with coconut oil every morning in addition to their usual oral hygiene routine. Participants underwent dental examinations at the start of the study and also after 7, 15 and 30 days. After one week of coconut oil pulling, there was a significant decrease in indices of plaque and gingivitis. After a month, the average gingivitis score decreased by 56% and the average plaque score decreased by 68%.
Method: Perform oil pulling as soon as you wake up, before brushing your teeth or eating. Put a tablespoon of coconut oil in your mouth. Swish it around your entire oral cavity and push it between your teeth. After 15-20 minutes when your whole mouth is coated with oil, spit the remainder into the trash. (Do not spit it into your sink since coconut oil is solid at room temperature, and could block your drain.)
Recommended:
- Coconut Oil – Oil Pulling, Bad Breath, Teeth Whitening, Dry Mouth
- Ayurvedic Oil Pulling Oil – Daily Swish, Mint
6. Reduces Inflammation
Inflammation plays a role in a wide range of disorders including allergies, asthma, arthritis, eczema, inflammatory bowel disease and cardiovascular disease.
The standard Western diet, high in omega-6 grains and oils, promotes inflammation throughout the body. Coconut oil is low in omega-6 and the MCTs and antioxidants it contains have been shown to reduce inflammation.
In a laboratory study, researchers extracted polyphenols from virgin coconut oil and injected them into rats with induced arthritis. The solution reduced swelling along with a range of inflammation indicators. It also inhibited the expression of inflammatory genes. The researchers compared the effects of the coconut polyphenols to those of Indomethacin, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug often prescribed for arthritis. The coconut oil solution was found to be more effective at reducing inflammation.
In a small study, 11 women were assigned to one of three diets. All had the same nutrient composition except for the fat and carbohydrate content and type of fatty acids. The women were assigned to either a low-fat diet with coconut oil, a high-fat diet with coconut oil or a high fat diet containing a commercial margarine. The participants followed each diet for 3 weeks, ate normally for a week and then switched to another experimental diet. Blood tests showed the lowest levels of inflammation markers when women consumed the high fat coconut oil diet. The coconut oil diet was also associated with lower levels of an antigen linked to heart disease.
Recommended:
7. Protects Your Liver
Rodent studies suggest that the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of coconut oil may work synergistically with the MCTs to protect the liver from toxins. In one study, mice who were fed coconut oil after being exposed to a toxic drug used in chemotherapy, showed an increase in beneficial liver enzymes and a decrease in inflammatory liver markers.
In a study published in the Journal of Nutrition, rats were divided into 8 treatment groups. Four groups were fed either a diet containing polyunsaturated corn oil or diets containing 10, 20 or 30% of calories from MCT oil. The other four received the same diets with alcohol substituting for carbohydrates. After 70 days, markers of liver disease were assessed. As the amount of MCT saturated fat in the diet increased, all measures of alcohol-induced liver pathology, including fatty liver disease, were progressively reduced. There was an almost complete elimination of liver disease in the rats who consumed a diet with 30% MCT saturated fat.
In another rodent study, researchers investigated the protective effects of coconut oil against liver damage caused by an overdose of paracetamol (the active ingredient in painkillers such as Tylenol). The rats were pretreated with oral administration of a saline solution or different volumes of virgin coconut oil before being fed a toxic dose of the analgesic. Rats who received the largest dose of coconut oil showed a significant reduction in liver damage compared to the control group. The researchers theorize that the liver-protective effect of coconut oil is due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Recommended:
Coconut Oil versus ‘Virgin’ Coconut Oil
Coconut Oil

If you buy a product simply labeled ‘coconut oil’, it was most likely made from copra. Copra is a dried coconut product used for oil extraction and cattle feed. It is also processed into soaps and cleaning products.
Copra oil is referred to in the industry as RBD (refined, bleached and deodorized). These processes do not necessarily involve any toxic chemicals. Bleaching refers to filtering the oil through clay to remove impurities. Heat or steam is used to deodorize the oil.
Coconut oils labeled ‘expeller-pressed’ have been extracted mechanically, whereas oils without these words on the label have probably been extracted with chemical solvents.
The RDB process results in a bland-tasting coconut oil with very little odor. It also depletes some of the antioxidants. However, RBD oil retains its healthy MCTs and its full profile of fatty acids.
Recommended:
- Coconut Oil for Skin or Hair – Premium Fractionated
- Coconut Oil, Carrier Oil
- Coconut Oil – Refined
- Coconut Oil Soap – Unscented
‘Virgin’ Coconut Oil

The definition of ‘virgin’ or ‘extra virgin’ coconut oil varies by brand. There is no certification body that guarantees that coconut oil can only be labeled ‘virgin’ if it meets specific criteria. That said, the term ‘virgin’ generally indicates an oil is made from fresh coconut.
Most brands of ‘virgin’ coconut oil are mass-produced. Fresh coconut is dried and put through a hydraulic press. The extracted liquid is then passed through a high-speed centrifuge to separate the oil from the milk.
Virgin coconut oil labeled ‘wet milled’ skips the drying process and uses liquid pressed from chunks of fresh coconut meat.
Some virgin coconut oils are marked as ‘raw’, meaning that no heat was used in processing the oil. Although ‘raw’ coconut oil is marketed as a healthier option, the evidence actually points in the opposite direction.
A 2013 study published in Food Science and Biotechnology found that antioxidant activity in hot extracted virgin coconut oil was 80-87% compared to 65-70% for cold extracted virgin coconut oil and 35-45% for RBD coconut oil. The same study found that HDL cholesterol increased by approximately 21% in rats who were fed hot extracted virgin coconut oil for 30 days, but did not significantly increase in rats fed raw or RDB coconut oil.
Recommended:
The Verdict
If you’re using coconut oil for its health benefits, virgin coconut oil is probably worth paying more for. However, don’t let the hype convince you that raw virgin coconut oil is even better. When purchasing coconut oil, always read the label and do research online to find out how it was processed.
Keep in mind that, while the cheap coconut oil available at supermarkets may have been made using chemical solvents, the same is true for any commercial vegetable oil not labeled ‘cold pressed’ or ‘virgin’.
You’ll still get the beneficial effects of a low omega-6 oil with high levels of MCTs if you substitute cheap coconut oil for corn oil, soybean oil or sunflower oil.
Final Word
If you want to experiment with the benefits of coconut oil, keep a jar in your kitchen for culinary uses and another jar in your bathroom for skin care and oral health.
Because coconut oil is saturated, it can withstand high cooking temperatures. Use it instead of vegetable oils for frying, roasting and sautéing. Substitute coconut oil for butter or shortening in baking and pastry-making.
If you use a commercial moisturizer, try using coconut oil on your skin instead. If you use an antiseptic mouthwash, try oil pulling and see if it makes a difference.









please i love to more about coconut soap and the making, thanks.