Fragrant plants have been used in folk medicine for thousands of years across many cultures. Methods for capturing the ‘essence’ of plants were first discovered in the Middle Ages.
Essential oils are distilled or extracted from large quantities of flowers, leaves, peels, resin, bark or roots. For example, it takes about 220 pounds of lavender flowers to make one pound of lavender oil.
This makes essential oils a highly concentrated source of phytochemicals. Phytochemicals help the plants thrive and also wards off unwanted pathogens. Each type of oil has a different chemical composition that affects its scent and its benefits for mental or physical health.
Scientists are exploring the use of essential oils in the treatment of various disorders, especially where the standard drug therapy has unwanted side effects.
Different essential oils can be inhaled, used topically or, in some cases, taken orally. Oils are helpful in treating a wide range of conditions due to their variety of phytochemicals they each contain. These 12 essential oils and 3 carrier oils described below all have health benefits supported by scientific research.
12 Essential Oils & Their Benefits
1. Lavender Oil

An old folk remedy for insomnia is to sleep on a pillow stuffed with lavender flowers. Research has confirmed that lavender oil is an effective sleep aid.
It seems to work by slowing the activity of the central nervous system. Inhaling the scent of lavender has a relaxing, soothing effect which can also help improve symptoms of anxiety.
The scent of lavender has even been used to calm fearful patients in dentists’ waiting rooms. Lavender oil also has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties that allow it to be used as an effective pain reliever.
Insomnia
Researchers at the University of Minnesota investigated the impact of lavender oil on 79 students who reported having sleep issues. All of the participants filled in questionnaires that asked about their quality of sleep and general well-being. They were also taught to practice good sleep hygiene.
In this randomized controlled trial, half of the students received a lavender inhalation patch and half received a placebo patch to wear on their chest in bed. After 5 nights of sleeping with the patches, the participants repeated filling in the questionnaires. Compared to the control group, the lavender oil group showed a significant improvement in scores for sleeping well, feeling energized and having vibrant senses, as well as an overall improvement in well-being.
Anxiety
A controlled clinical study published in the journal Phytomedicine tested the efficacy of a lavender oil supplement for patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). GAD affects 6.8 million adults in the United States. It is characterized by excessive and persistent worrying and frequently expecting the worst.
GAD is often treated with benzodiazepine drugs which induce sedation and can be addictive. Researchers randomized GAD patients into 2 groups. One received a common benzodiazepine (lorazepam) and the other received lavender oil capsules. All participants completed a standard anxiety symptoms rating scale before and after the treatment.
After 6 weeks, both groups had an almost identical reduction in overall anxiety scores: 45% for the lavender oil group and 46% for the lorazepam group. Physical and psychological anxiety symptoms both decreased to a similar extent in the 2 groups. The lavender oil supplement was shown to be just as effective as the drug treatment with no risk of addiction or drowsiness.
Period Pain
A clinical trial examined the effects of aromatherapy massage with lavender oil on menstrual pain and cramps in 80 nursing and midwifery students. All of the participants rated their pain on the first day of their periods as six out of ten or above.
The patients were instructed to phone the researchers when they were feeling pain at the onset of menstruation. They then received a 15-minute abdominal massage with either lavender oil (diluted with almond oil) or with a placebo oil. They rated their pain both before and after the massage.
The next month, each patient received the alternative treatment. Pain scores were significantly lower following the lavender massage compared to the placebo massage.
Another study found that simply inhaling the scent of lavender oil significantly decreased period pain compared to inhaling a placebo oil.
Acute Pain
Kidney disease patients experience severe pain when large needles are inserted at the start of every dialysis session.
A crossover study published in Complementary Therapies in Medicine tested the effects of lavender oil on 34 dialysis patients. The intensity of pain for each patient was measured with a numeric rating scale during the insertion of arterial needles under 3 different conditions.
In one session, there was no intervention. In another, 100% lavender oil was applied to the skin at the needle site. In a third session, a placebo was applied to the skin. Lavender oil significantly reduced patients’ intensity of pain compared to no intervention or placebo.
Recommended:
2. Peppermint Oil

Peppermint has long been used to soothe an upset stomach. It has an antispasmodic effect which calms the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract and allows food and digestive gas to pass through the system more quickly.
It also helps the body to digest fats by increasing the flow of bile. Research has shown that peppermint oil capsules are an effective treatment for dyspepsia and IBS.
When applied topically, the menthol in peppermint oil stimulates cold receptors in the skin. This sensation helps soothe itchy, irritated skin, making peppermint oil a good home remedy for insect bites or hives.
Topical peppermint oil has another, somewhat surprising use. It promotes hair growth by stimulating the dermal papilla and increasing blood circulation to the hair follicles.
Indigestion
Dyspepsia is a common condition caused by impaired digestion which may include symptoms such as discomfort after eating, abdominal pain, bloating, heartburn, nausea or belching up food.
A German study compared the effects of a peppermint oil supplement to cisapride, a drug which increases the speed of digestion and is used to treat gastric reflux.
Researchers randomized 118 outpatients with dyspepsia into 2 groups. One group received capsules containing 90 mg of peppermint oil and 50 mg of caraway oil. The other received the recommended dose of cisapride.
Pain scores were measured before and after 4-weeks of treatment. Both groups of patients had a statistically equivalent reduction in intensity of pain, frequency of pain and other dyspeptic symptoms.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
A systematic review published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology assessed the safety and efficacy of peppermint oil capsules in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Researchers analyzed data from 9 randomized placebo-controlled trials including 726 IBS patients.
Peppermint oil was found to be significantly superior to a placebo in improving overall IBS symptoms and abdominal pain. Side effects of peppermint oil were mild and transient. Researchers concluded that peppermint oil capsules are a safe and effective treatment for IBS.
Hair Growth
A rodent study published in Toxicological Research compared the effects of peppermint oil to the popular hair regrowth treatment minoxidil (Rogaine).
Researchers shaved the backs of 20 mice to expose bald skin. The mice were then randomized into 4 groups based on different topical applications: salt water, jojoba oil, peppermint oil diluted in jojoba oil and minoxidil. Each solution was applied to the shaved backs of the mice once a day for 4-weeks.
At the end of the study, researchers used fluorescent microscopy to observe and measure the number, elongation, thickness and depth of hair follicles.
Mice in the peppermint oil group showed the most prominent hair growth, and their hair grew back faster than mice treated with minoxidil. Compared to the other treatment groups, they had a significant increase in follicle number, follicle depth and dermal thickness. Researchers concluded that peppermint oil could be used as a therapeutic alternative medicine for hair loss in humans.
Recommended:
3. Lemon Balm (Melissa) Oil

Lemon Balm (also known as Melissa), is known for its calming properties. In the middle ages, it was grown in monastery apothecary gardens and used as a sleep aid and general panacea.
Lemon balm contains compounds called terpenes that act on neurotransmitters in the brain to produce a relaxing effect. Lemon balm oil has been shown to reduce negative reactions to stressful situations and calms agitation in people with dementia.
Stress
A cross-over study investigated the effects of lemon balm on laboratory-induced stress in 18 healthy volunteers. Each participant received a 300mg dose of lemon balm extract, a 600mg dose of lemon balm extract and a placebo given in random order on 3 separate days.
They then completed a 20-minute computer test called the Defined Intensity Stressor Simulation (DISS) battery. The DISS presents 4 tasks at once via a split screen and requires participants to attend to them simultaneously while their speed and accuracy is scored. The test has been shown to increase negative mood, arousal and stress.
Results showed that the 600mg dose of lemon balm counteracted the negative mood effects of the DISS, with significantly increased ratings for calmness and reduced alertness. Moreover, when participants ingested the 300mg dose of lemon balm, their speed of mathematical processing increased with no reduction in accuracy.
Dementia
A randomized placebo-controlled trial published in the Journal of Clinical Psychology investigated the effects of lemon balm aromatherapy on 72 patients with severe dementia. Care staff applied a topical oil to the patients’ faces and arms twice daily. The active treatment group received lemon balm oil combined with a base lotion, while the control group received sunflower oil. Clinically significant agitation and quality of life indices were monitored over the 4-week trial period.
In the lemon balm group, 35% of patients had an overall improvement in agitation compared to 11% in the placebo group. Quality of life also improved significantly for patients who received lemon balm. They spent less time socially withdrawn and more time engaged in constructive activities.
Recommended:
4. Copaiba Oil
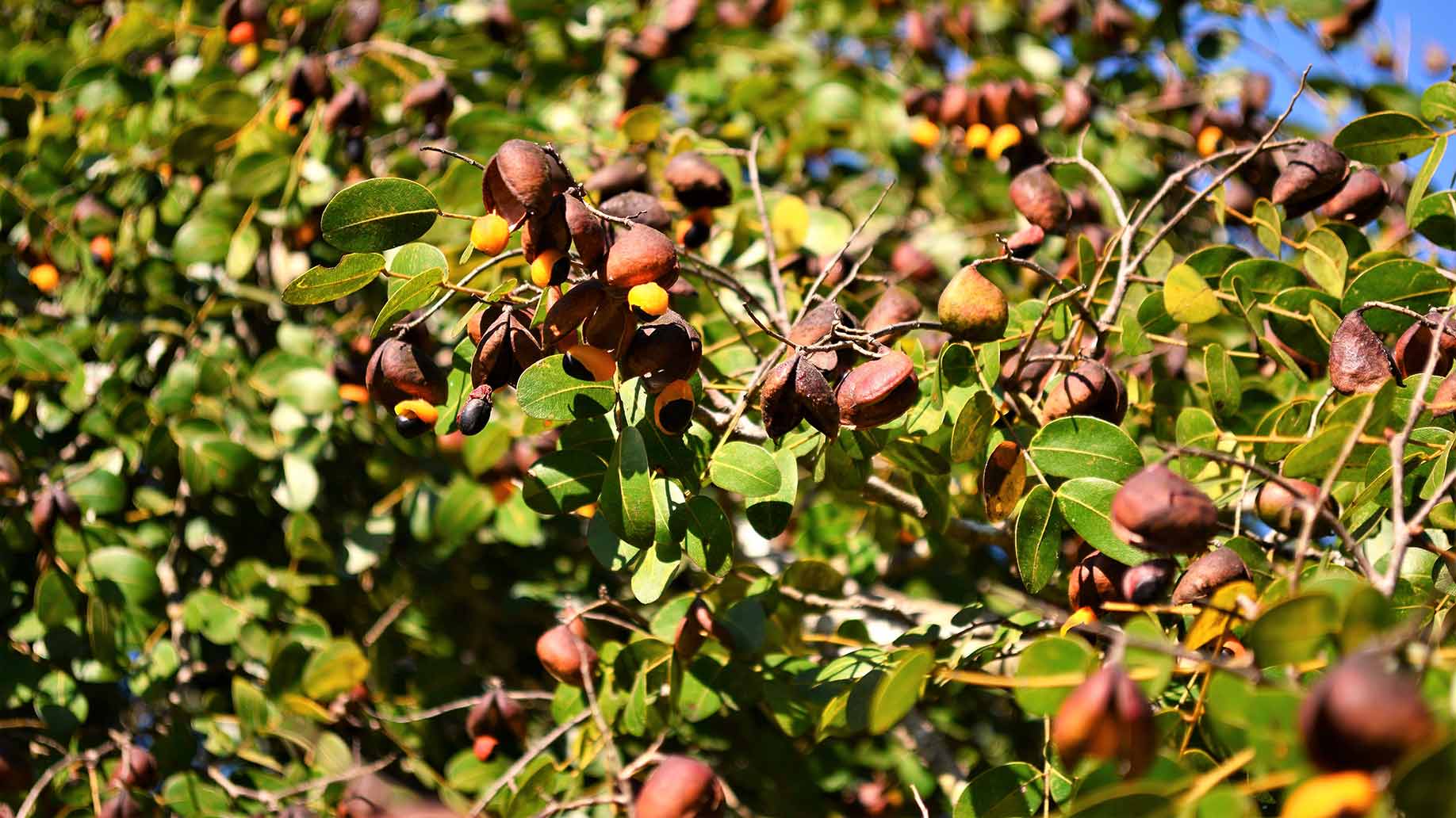

Copaiba oil is distilled from resin secreted by trees in the genus Copaifera which grow in the Amazon rainforest. Copaiba resin has been used medicinally by South American natives for hundreds of years.
The copalic acid in copaiba oil halts the growth of several species of dental bacteria and research has focused on its potential applications in dentistry.
Copaiba oil has anti-inflammatory properties and is often marketed as a treatment for arthritis, however most of the evidence for its efficacy comes from rodent studies. A 2017 review published in Integrative Medicine pointed out that copaiba had not yet been tested in a randomized trial against a placebo in human arthritis patients or tested in comparison to anti-inflammatory medications.
Oral Health
A Brazilian study evaluated the antibacterial activity of copaiba oil on common microorganisms found in dental plaque. Samples of 3 strains of Streptococcus bacteria were collected from adult volunteers with cavities and gingivitis for testing. The researchers also tested standard strains of 4 other types of dental Streptococcus.
The bacteria were incubated for 24 hours in Petri dishes containing either copaiba oil, chlorhexidine (an antiseptic) or a base gel used as a control. The copaiba oil gel demonstrated antibacterial activity against all the strains of Streptococcus tested and performed better than chlorhexidine against Streptococcus mitis.
Inflammation
In a study published in the Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, researchers investigated the action of copaiba oil on arthritis in rats. The rats were fed copaiba oil at either a high or low dose for 18 days. Both doses improved paw swelling and presented systemic anti-inflammatory and antioxidant action. However, the researchers also found evidence of liver damage in healthy control rats who were fed copaiba oil.
In another study, researchers evaluated the anti-inflammatory and healing effect of copaiba oil treatment on injuries to rats’ tongues. They found that copaiba oil reduced inflammation by decreasing the number of white blood cells infiltrating the injured tissue.
Recommended:
5. Bergamot Oil
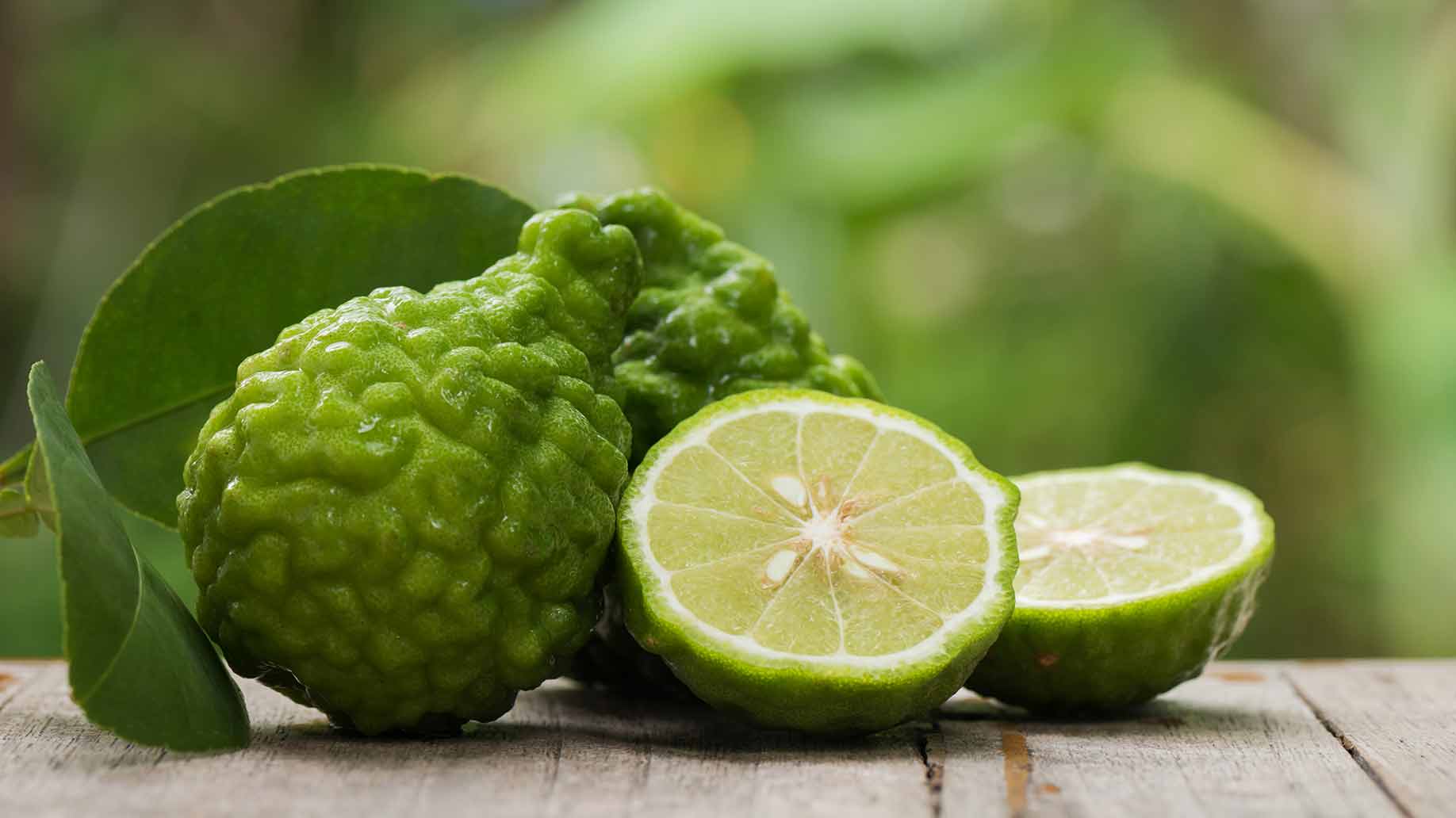

Bergamot is a Mediterranean citrus fruit with a distinctive spicy scent. Bergamot essential oil is widely used in aromatherapy to reduce stress and anxiety.
Anxiety
Research has shown that inhalation of bergamot oil can be just as effective as the benzodiazepine drug diazepam for reducing anxiety.
Heart Disease
In the south of Italy, bergamot juice is a folk remedy for heart problems. Research indicates that specific flavonoids in bergamot, which are not found in other citrus fruits, can help to lower cholesterol and reduce the risk for heart disease.
Stress
A Japanese cross-over study examined the effects of aromatherapy with bergamot oil on mood and stress-levels in 41 female university students. Each of the participants was exposed to 3 experimental conditions in random order.
In one scenario, they simply rested for 15 minutes, in another, a diffuser filled the air with water vapor as they rested, and in a third, a diffuser filled the room with water vapor containing bergamot essential oil. After 15 minutes, saliva samples were collected and the volunteers completed questionnaires about anxiety and mood.
Following the bergamot aromatherapy session, the participants had significantly lower levels of the stress hormone, cortisol. They also had lower scores for anxiety, anger, confusion and physical and mental fatigue.
High Cholesterol
A study published in Frontiers in Pharmacology investigated the effects of a bergamot flavonoid extract supplement on 80 men and women with moderately high cholesterol. All of the participants were given a daily dose of the bergamot extract for 6 months.
At the start and end of the study, their cholesterol levels were measured with a blood test and the thickness of their arterial walls were measured with an ultrasound scan.
Six months of bergamot supplementation significantly reduced total cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL ‘bad’ cholesterol, while HDL ‘good’ cholesterol significantly increased. Small, dense LDL, the most dangerous kind of cholesterol, decreased by 67%. Arterial wall thickness, a sign of atherosclerosis, also significantly decreased.
Recommended:
6. Neroli Oil
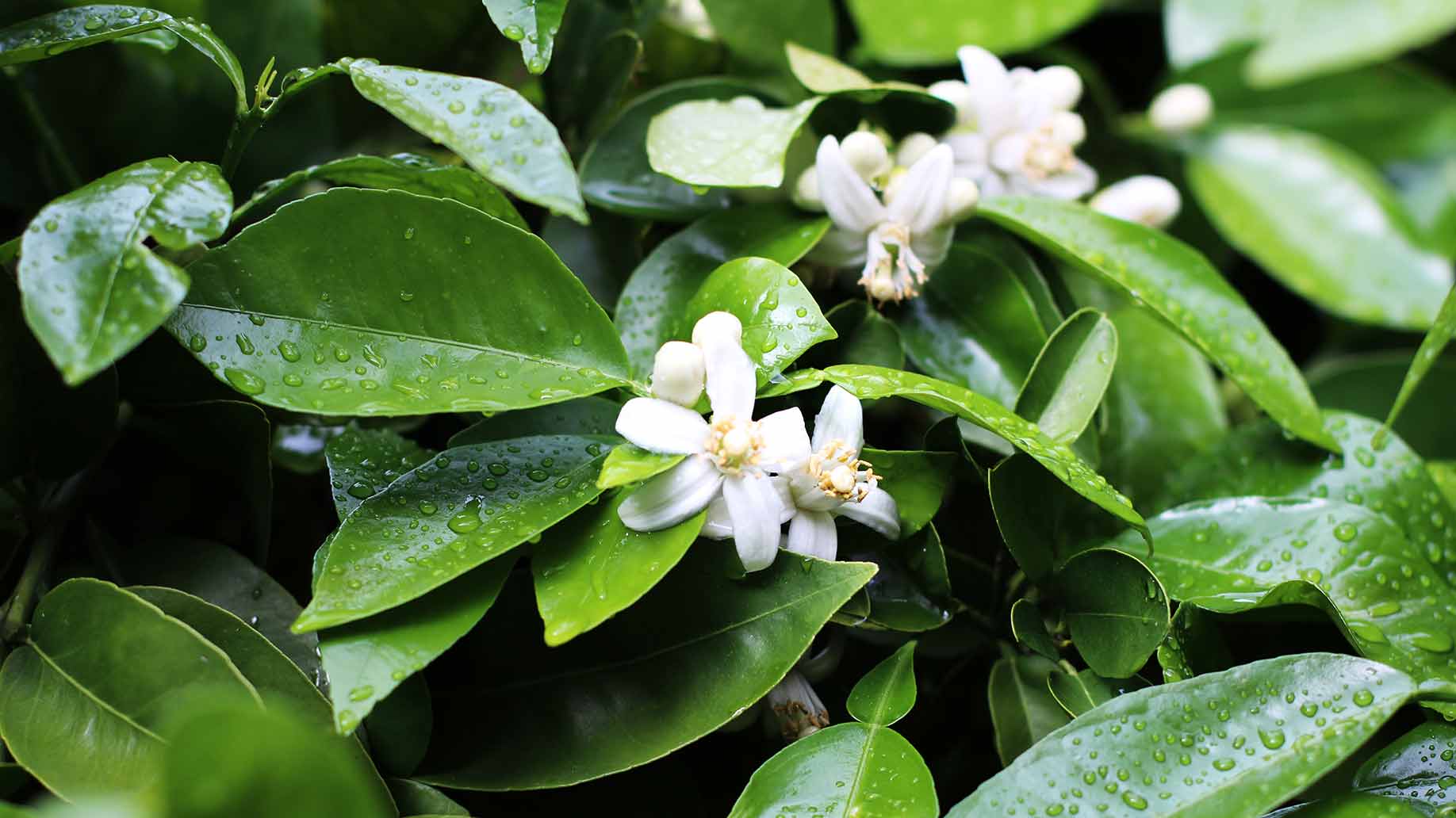

Neroli oil is distilled from the fragrant blossom of the bitter orange tree, Citrus aurantium, which is native to tropical and subtropical Asia.
Research on mice has shown that limonene, one of the major chemical components of neroli, acts as a muscle relaxant and has a sedative effect. Neroli oil aromatherapy can help lower blood pressure and relieve symptoms associated with menopause.
Menopause Symptoms
A Korean study investigated the effects of neroli oil inhalation on 63 postmenopausal women. The participants were randomly assigned to 3 groups. One received a 1% solution of neroli oil diluted with almond oil, one received a 5% solution of neroli oil and a control group received pure almond oil.
Each woman was instructed to sit in a comfortable place, pour the oil onto a fragrance pad, hold the pad near their nose and inhale the scent for 5 minutes. The subjects self-treated twice a day for 5 days. The women took blood pressure tests and completed menopause symptom questionnaires before and after the aromatherapy treatment.
Compared to the control group, both neroli oil groups had significant improvements in physical symptoms of menopause. The 5% neroli oil group had significantly lower systolic blood pressure, and both neroli groups had significantly lower diastolic blood pressure. Interestingly, both neroli oil groups also had a significant increase in sexual desire.
Recommended:
7. Tea Tree Oil
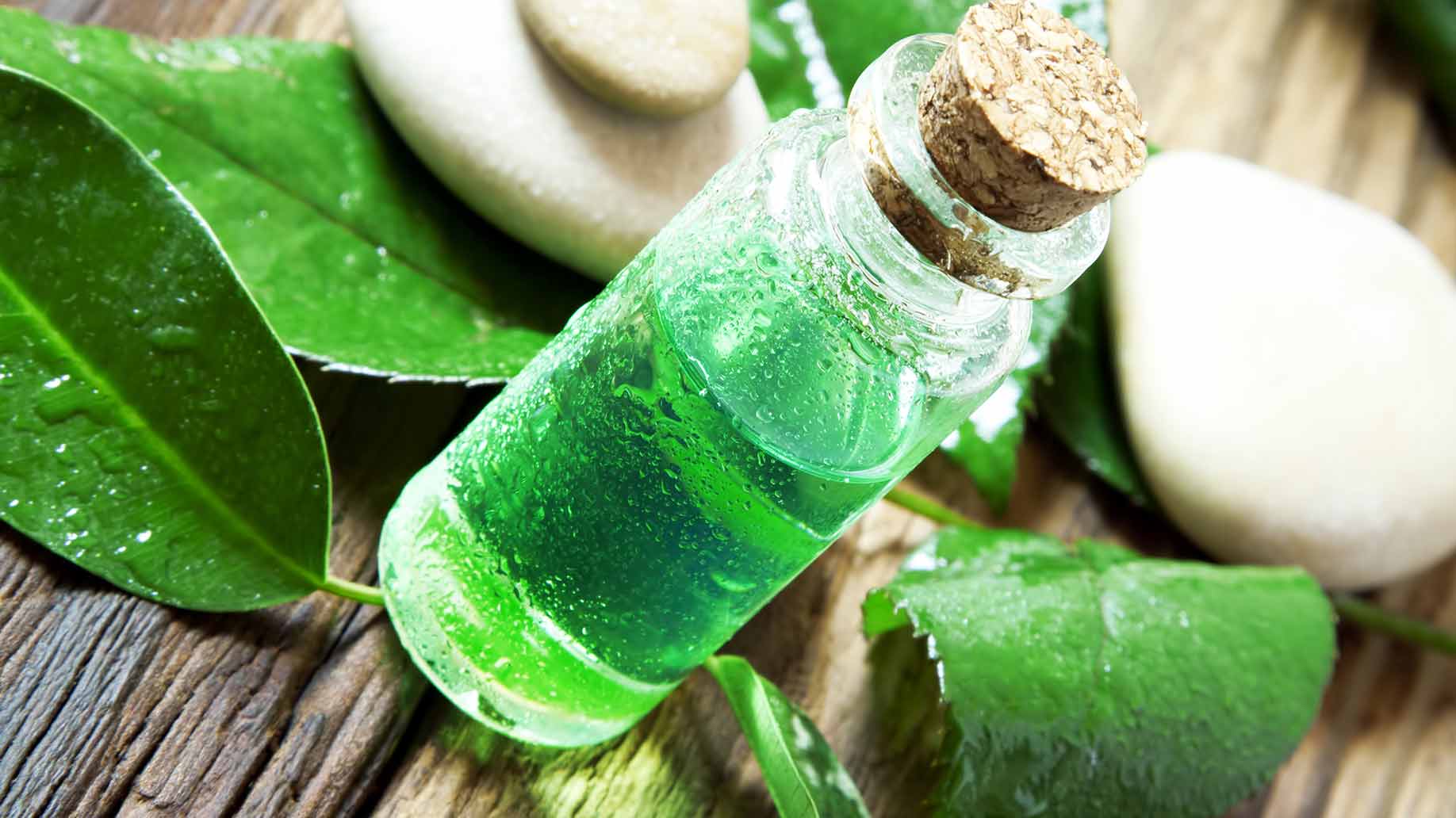

Tea tree oil is made from the leaves of the Australian tea tree plant. Aboriginal people used tea tree leaves for treating wounds and preventing infections.
Tea tree oil has antibacterial, anti-fungal and antimicrobial properties which makes it a useful treatment for a number of skin conditions. It is also a natural insecticide and is even used in commercial head lice treatments.
Athlete’s Foot
A study published in the Australasian Journal of Dermatology investigated the efficacy of tea tree oil for treating athlete’s foot. Participants were randomly assigned to receive a 25% tea tree oil solution, a 50% tea tree oil solution or a placebo solution.
All 158 athlete’s foot patients were instructed to apply the solution to the affected area twice daily. After 4 weeks, there was a marked clinical response seen in both of the tea tree oil groups. The cure rate for patients in the 50% tea tree group was 64%, compared to 31% in the placebo group.
Acne
A randomized, placebo-controlled study examined the efficacy of tea tree oil for treating mild-to-moderate acne. A total of 60 acne patients were divided into 2 groups. One group received a 5% tea tree oil gel and the other received a placebo gel.
The patients were instructed to apply the gel twice daily for 20 minutes and then to wash it off. After 45 days, patients in the tea tree oil group has significantly less acne than those in the placebo group. Tea tree oil was nearly 4 times more effective at reducing the number of pimples and pustules and nearly 6 times better at reducing acne severity.
Dandruff
A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology tested the efficacy of tea tree oil in 126 patients with mild-to-moderate dandruff. The participants were randomly assigned to receive either 5% tea tree oil shampoo or a placebo shampoo, which was used daily for 4-weeks.
The tea tree oil groups showed a 41% improvement in dandruff severity compared with 11% in the placebo group. Patients’ self-assessment scores for itchiness and greasiness also significantly improved in the tea tree oil group.
Fungal Nail Infections
A study published in the Journal of Family Practice compared the effectiveness of tea tree oil and the anti-fungal medication clotrimazole for the treatment of fungal infections. The participants included 117 patients diagnosed with fungal infections of the toenail. The patients were randomized into 2 groups.
One received a 100% tea tree oil and the other received a standard 1% clotrimazole solution applied twice daily. After 6 months, results for the 2 treatments were almost identical with 61% of the clotrimazole group and 60% of the tea tree group showing partial or full resolution. Three months later, 55% of the clotrimazole group and 56% of the tea tree group reported continued improvement or resolution.
Head Lice
An Italian study investigated the efficacy of tea tree oil and nerolidol against head lice and their eggs. The substances were tested at different concentrations on 69 head lice and 187 louse eggs collected from school children. A 1% concentration of tea tree oil killed 100% of head lice in 30 minutes.
Nerolidol is a natural plant compound found in many essential oils, including tea tree. The researchers found that a combination of a 0.05 % concentration of tea tree oil and a 1% concentration of nerolidol produced the death of all head lice in 30 minutes and prevented louse eggs from hatching after 5 days.
Recommended:
8. Rose Oil

Rose oil is steam distilled from the petals of the damask rose or cabbage rose.
Laboratory research has shown that rose oil contains the antioxidants tocopherol and carotene. Rose oil demonstrates strong antibacterial activity against several different strains. It can also be used in aromatherapy to promote a calm mood.
Anxiety
A rodent study compared the effects of rose oil inhalation to the effects of the anti-anxiety drug diazepam. Rats have a natural tendency to prefer hidden, closed spaces to open, exposed spaces. The more anxiety they experience, the more likely they are to hide. The researchers found that rose oil inhalation significantly increased the number of visits to and time spent in the open arms of a maze. The anti-anxiety effect was similar to diazepam.
A Thai study investigated the effect of rose oil on 40 human volunteers. The rose oil was absorbed through the skin and the participants wore breathing masks to prevent them from inhaling the scent.
Compared to a placebo, rose oil caused significant decreases in systolic blood pressure and breathing rate. Participants in the rose oil group rated themselves as calmer, more relaxed and less alert than subjects in the control group.
Recommended:
9. Oregano Oil

Oregano is a familiar herb used in Mediterranean dishes. The essential oil distilled from its leaves and flowers contains a phytochemical called carvacrol which has powerful antibacterial and anti-fungal properties.
Food Poisoning
A study published in the Journal of Food Protection investigated the antimicrobial activities of carvacrol against antibiotic-resistant Salmonella. Celery and oysters were inoculated with the resistant strain. A 1% carvacrol solution rapidly reduced the Salmonella population on celery to below detection. In infected oysters exposed to carvacrol, the bacteria population was 100,000 times smaller after 3 days.
Fungal Infections
A laboratory study assessed the anti-fungal activity of constituents of essentials oils against oral candida. This fungus causes an infection known as denture stomatitis, in which the area of the mouth covered by dentures becomes inflamed.
The researchers tested 10 organic compounds against 10 strains of candida collected from denture wearers. Carvacrol was classified as very active against oral candida. Researchers concluded that it might be a promising alternative for a topical treatment for denture stomatitis.
Recommended:
10. Eucalyptus Oil

Many species of eucalyptus trees are used in Brazilian folk medicine for the treatment of medical conditions such as cold, fever, flu and bronchitis. In the modern Western world, eucalyptus oil is commonly used as a home remedy for colds.
Cold, Cough & Flu
Eucalyptus oil is added to a bowl of boiling water. The steam acts as an expectorant and decongestant. Laboratory research has shown that eucalyptus oil has antibacterial, anti-fungal and antiviral properties. Other studies have shown that it is an anti-inflammatory agent and an effective analgesic.
Asthma
A study published in the Journal of Asthma tested the benefits of cineole, the active ingredient in eucalyptus oil, for asthma patients. A total of 247 patients with confirmed asthma were selected for the study. The patients were randomly assigned to receive either a placebo or 200 mg of cineole, 3 times per day in addition to their usual asthma medication.
After 6 months, the patients who received cineole supplements showed significantly more improvements to lung function, asthma symptoms and quality of life compared to the control group.
Recommended:
11. Clove Oil

Clove oil has antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-fungal, antiviral, anti-inflammatory and anesthetic properties. It has long been used as a traditional home remedy for toothaches.
Oral Health
It’s major active component, eugenol, is widely used in dental materials such as temporary fillings. Clove oil is also found in oral health products such as toothpaste and mouthwash. Most of the research on clove oil has been done in the context of its applications in dentistry.
Pain
A study published in the Journal of Dentistry examined whether clove was an effective topical anesthetic. A total of 73 adult volunteers were randomized to have one of four substances applied to their gums: benzocaine 20% gel (a local anesthetic), homemade clove gel, a placebo that resembled benzocaine or a placebo that resembled clove.
After 5 minutes, each subject received 2 needle sticks and rated their pain on a scale ranging from none-to-very severe. The clove and benzocaine gels both had significantly lower pain scores than the placebos. There was no significant difference in pain scores between clove and benzocaine.
Tooth Protection
Fruit juices contain acids and sugars that can dissolve dental enamel, leading to tooth sensitivity, erosion and decay. Clove oil contains eugenol and eugenyl acetate, both of which are used in dental care.
A laboratory study published in the International Journal of Dentistry investigated the effect of clove essential oil on tooth erosion caused by apple juice. Human tooth specimens were treated with one of 4 substances: clove oil, eugenol, eugenyl acetate or fluoride. A control group received no treatment.
The teeth were then soaked in apple juice for 24 hours. All of the substances significantly decreased the decalcification of tooth enamel by apple juice compared to the control group. Clove oil was more effective than either of its active components alone. There was no statistically significant difference between the fluoride and clove oil treatment group.
Recommended:
12. Sage Oil

The name sage comes from Latin word ‘salvere’ meaning ‘to save’. The herb has a long history of medicinal (as well as culinary) use.
Sage essential oil has antibacterial, anti-fungal, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. In aromatherapy, sage oil is used to stimulate the mind and help fight mental fatigue. Researchers are exploring the use of sage for treating the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. Compounds in sage leaves also affect fat metabolism and can help to lower cholesterol.
Alzheimer’s Disease
A randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics tested the use of sage extract for treating patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
A total of 42 patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease were divided into 2 groups. The treatment group received 60 drops of sage extract per day and the control group received a placebo. After 4 months, the sage group performed significantly better on cognitive function tests than the placebo group. They also appeared to be less agitated.
High Cholesterol
A study published in Complementary Therapies in Medicine evaluated the use of sage extract for treating high cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes.
A total of 80 patients were randomized to receive either a 500 mg sage leaf extract capsule or a placebo capsule daily. After 3 months, the diabetics who took the sage supplements had significantly lower levels of LDL ‘bad’ cholesterol and higher levels of HDL ‘good’ cholesterol. They also had significantly lower blood sugar levels compared to the placebo group.
Recommended:
Carrier Oils
Carrier oils help to evenly distribute essential oils into the skin. They are used to dilute essential oils, allows essential oils to be absorbed further and makes them safer for topical application.
Carrier oils are made from vegetable oils. The best carrier oils are cold-pressed and made from plant sources. Unlike essential oils, carrier oils do not have a concentrated fragrance. However, some have a mild pleasant scent. Examples of carrier oils include:
- Olive oil
- Walnut oil
- Sweet almond oil
- Avocado oil
- Coconut oil
- Cocoa Butter
The carrier oils described below all have therapeutic properties that can augment the benefits of the essential oils that are added to them.
1. Argan Oil

Argan oil is extracted from the nut of the Moroccan argan tree. Argan is a popular carrier oil for diluting essential oils.
Argan oil is an edible virgin oil with cholesterol-lowering properties, similar to olive oil. It also contains benefits for hair and skin and is used as an ingredient in commercial shampoos, moisturizers and cosmetics.
Skin Care
A study published in Clinical Interventions in Aging investigated the effects of argan oil on postmenopausal skin elasticity. A total of 60 postmenopausal women were randomly assigned to consume 25 ml of either dietary argan oil or olive oil daily.
Both groups were instructed to apply cosmetic argan oil to their left forearm every night. After 60 days, assessments of skin elasticity were performed on both forearms. Both consumption and topical application of argan oil led to a significant increase in all measures of skin elasticity.
A study in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology evaluated the efficacy of a sebum control cream containing argan oil for treating oily skin. Researchers recruited 20 volunteers with greasy facial skin and instructed them to apply the test product twice daily for 4-weeks.
Clinical assessment of sebum levels decreased by 33% and areas covered with oily spots decreased by 42%. Questionnaires revealed that 95% of subjects noticed a visible improvement.
Recommended:
2. Jojoba Oil

Jojoba oil is produced from the seeds of a woody desert plant native the southern US and northern Mexico. Technically, it is not an oil but a liquid wax. As such, it is a stable carrier for essential oils and does not feel greasy on the skin.
Native Americans used jojoba to help wounds heal. Laboratory research on skin cells has shown that jojoba liquid wax stimulates collagen production and accelerates wound closure.
Acne
A German pilot study assessed the benefits of self-treatment with clay jojoba oil masks on 133 participants with acne. The participants applied the jojoba oil facial masks at home, 2-3 times a week for 6-weeks.
At the beginning and end of the study, they were asked to count their facial pimples, pustules, blackheads and cysts. There was a 54% average reduction in acne counts, averaging 7 blemishes decreasing to 3.
Recommended:
3. Grapeseed Oil

The grape seeds used in grapseed oil are a byproduct of the wine-making industry. Grapeseed oil is used as a cooking oil and is widely used in skin care products such as moisturizers and sunscreen.
When consumed, grapeseed oil may help prevent type 2 diabetes. In one study, overweight or obese women were assigned to a weight loss diet with 15% of calories from grapeseed oil. After 8-weeks, they had lower levels of insulin resistance and inflammation than a control group on a 15% sunflower oil diet.
When used topically, phenolic compounds in grapeseed oil can fight bacteria and accelerate wound healing.
MRSA
MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) is a ‘superbug’ notorious for causing infections that spreads throughout hospitals.
A laboratory study published in the Journal of Toxicological Sciences measured the antibacterial activity of grapeseed extract against 43 strains of MRSA. A concentration of 3 mg/ml grapeseed extract completely inhibited all of the bacterial strains tested.
Wound Healing
A rodent study published in Phytotherapy Research evaluated the wound healing properties of grapeseed oil. Identical wounds were treated with either grapeseed oil, cranberry oil, petroleum jelly or mupirocin ointment (a topical antibiotic).
Healing was assessed by the rate of wound contraction and levels of hydroxyproline, an amino acid that is a component of skin collagen. After 13 days, reduction of wound area was greatest in the cranberry oil and grapeseed oil groups. Hydroxyproline content was also significantly higher in the animals treated with plant oils.
Recommended:
How to Use Essential Oils
- To fill a room with therapeutic fragrance, add a few drops of oil to a candle diffuser, reed diffuser or electric diffuser.
- Alternatively, put a few drops of an essential oil on a handkerchief, hold it a few inches from your nose and breathe in.
- Make a therapeutic massage oil by adding 15 drops of essential oil to 1 ounce of any carrier oil.
- Make a skin cream by adding 15 drops of essential oil to 1 ounce of jojoba oil, coconut oil or cocoa butter.
- Make scented bath salts by mixing 1 pound of Epson salts with 15 drops of essential oil. Store in a glass jar and use half a cup of salts per bath.
Recommended:
Safety Warnings
- Never apply essential oils directly onto your skin. Always dilute them with water or a carrier oil. If you have any kind of skin reaction to an essential oil, discontinue use immediately. Wash the area off with warm water or rub a carrier oil over the irritated area.
- Some essential oils should not be taken orally. Most bottles will indicate if the oil is intended for oral or topical use. Essential oils that can be ingested need to be correctly diluted and dosed. Never swallow essential oils from the bottle. If you want to try taking peppermint oil for indigestion or lemon balm oil for stress, buy supplement capsules from a reputable brand and do not exceed the recommended daily dose.
Final Word
Many essential oils appear to have a synergistic effect, so experiment with different combinations. For example, lavender, lemon balm and bergamot all have a calming effect. Try putting a few drops of each into a diffuser for stress-relief after a long day.
One of the benefits of essential oils is that they come in small, portable containers. If you find that inhaling an oil helps with your symptoms, carry a bottle in your pocket or handbag. Put a few drops on a tissue and breathe in whenever you need a boost.
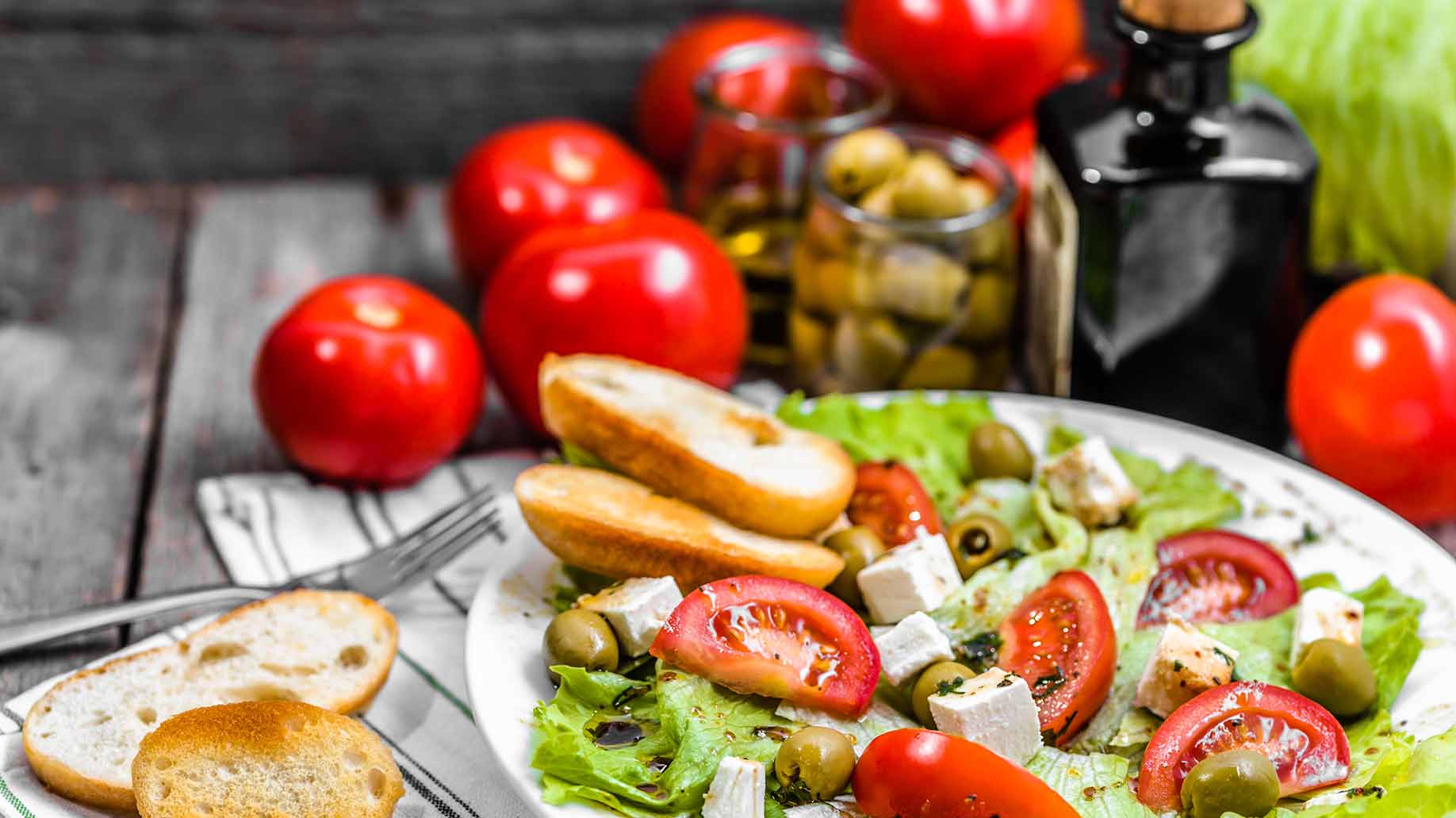






























































 A Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits and vegetables and low in omega-6 fats, has been associated with a lower prevalence of asthma and allergies. This could be due to antioxidants in the fruits and vegetables which seem to have a protective effect.
A Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits and vegetables and low in omega-6 fats, has been associated with a lower prevalence of asthma and allergies. This could be due to antioxidants in the fruits and vegetables which seem to have a protective effect.